The Facts Concerning Overpronation
The anatomy of a normal foot allows for both to occur at the same time. Approximately 30% of the population have a normal foot. The remainder of people either overpronate (95% of abnormal feet) or oversupinate (5% of abnormal feet). The important thing to know is that all feet pronate and supinate, but abnormal feet do one of these things too much or at the wrong time. When the foot overpronates or oversupinates, several foot ailments can develop.

Causes
Pronation can occur as an overuse syndrome in active runners, where a great deal of stress is placed on ligaments and tendons that support the medial column. Obesity is another predictor for pronation and deterioration of the medial ligaments and posterior tibial tendon due to excessive stress on these tissues. Acute Trauma can also lead to over-pronation when ligaments are torn or tendon is ruptured. Once again this can lead to a collapse of the medial column. Arthritic conditions involving the knee joint when the joint is in varus (inner collapse) posture, this places the center of gravity over the ankle joint rather than the foot causing undue pressure on the inner ankle.
Symptoms
Over-Pronation may cause pain in the heel of the foot, the foot arch, under the ball of the foot, in the ankle, knee, hip or back. The symptoms may be localized to one particular area of the foot or may be experienced in any number of combinations. Standing for long periods of time, walking and running may become difficult due to the additional stress and/or discomfort accompanied with these activities. Upon Visual Inspection, when standing the heels of the foot lean inward and one or both of the knee caps may turn inward.
Diagnosis
Look at the wear on your shoes and especially running trainers; if you overpronate it's likely the inside of your shoe will be worn down (or seem crushed if they're soft shoes) from the extra strain.

Non Surgical Treatment
Overpronation is a term used to describe excessive flattening of the plantar arch. Pronation is a normal part of our gait (the way we walk), and it comprises three movements: dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction. Dorsiflexion is the upward movement of the foot, eversion describes the foot rolling in, and abduction is ?out toeing,? meaning your toes are moving away from the midline of your body. When these three motions are extreme or excessive, overpronation results. Overpronation is very common in people who have flexible flat feet. Flatfoot, or pes planus, is a condition that causes collapse of the arch during weight bearing. This flattening puts stress on the plantar fascia and the bones of the foot, resulting in pain and further breakdown.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
Hallux Abducto Valgus Treatment
Overview
 Bunions are bony bumps that form on the side of the big toe joint or baby toe joint (these are commonly called ?bunionettes? or ?tailor?s bunions?). Bunions most commonly result from one or more of the following factors: genetics, faulty foot mechanics like over-pronation, and/or long periods of time spent in improperly fitting footwear. Bunions can start with audible clicking (called ?crepitus?) and/or stiffness in the affected joint which indicates that the joint surfaces are rubbing together improperly. This may progress to include inflammation, degeneration of the surfaces of the joint, deformity (including bone growth at the joint line and displacement of the toe) and ultimately, loss of range of motion in the joint.
Bunions are bony bumps that form on the side of the big toe joint or baby toe joint (these are commonly called ?bunionettes? or ?tailor?s bunions?). Bunions most commonly result from one or more of the following factors: genetics, faulty foot mechanics like over-pronation, and/or long periods of time spent in improperly fitting footwear. Bunions can start with audible clicking (called ?crepitus?) and/or stiffness in the affected joint which indicates that the joint surfaces are rubbing together improperly. This may progress to include inflammation, degeneration of the surfaces of the joint, deformity (including bone growth at the joint line and displacement of the toe) and ultimately, loss of range of motion in the joint.
Causes
Bunions may be hereditary, as they often run in families. This suggests that people may inherit a faulty foot shape. In addition, footwear that does not fit properly may cause bunions. Bunions are made worse by tight, poorly-fitting, or too-small shoes. Bunions may also happen due to inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. Anyone can get bunions, but they are more common in women. People with flat feet are also more likely to get bunions due to the changes in the foot caused by bunions. There is also a condition called adolescent bunion, which tends to occur in 10-to-15-year old girls.
Symptoms
Bunions may cause no pain at first. But as the big toe begins to turn in towards the other toes, people with bunions usually experience redness, pain, swelling, and tenderness in the area around the joint. Pressure inside the joint or from footwear pressing against the bunion may also cause discomfort. As the affected toe curves closer to the other toes on the foot, these toes can become painful as well. Complications of bunions include corns, calluses, hammer toe, and ingrown toenails. Other complications include irritation of the nerves surrounding the bunion area. Excess rubbing of the bunion against the footwear may lead to changes in the skin, resulting in corns or calluses. Hammer toe is a deformity of the toe immediately next to the big toe. A hammer toe is slightly raised and points upwards from the base and downwards at the end of the toe. Ingrown toenails can result from increased pressure from the big toe on the other toes. There may also be a decrease in the amount a person can move the joint affected by the bunion. Irritation of the nerves will feel like burning or decreased sensation.
Diagnosis
Bunions are readily apparent, you can see the prominence at the base of the big toe or side of the foot. However, to fully evaluate your condition, the Podiatrist may arrange for x-rays to be taken to determine the degree of the deformity and assess the changes that have occurred. Because bunions are progressive, they don't go away, and will usually get worse over time. But not all cases are alike, some bunions progress more rapidly than others. There is no clear-cut way to predict how fast a bunion will get worse. The severity of the bunion and the symptoms you have will help determine what treatment is recommended for you.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most common cause of a bunion is over pronation, this is when your foot rotates in too much as you walk. You really need to treat the underlying cause of the bunion as soon as possible to prevent any further damage. Wear wide fitting shoes, preferably with a leather upper which will allow a stretch. Avoid high heeled shoes. Bunion exercises will help to keep the joint flexible. Bunion surgery may be required in some patients, however this should only be considered when all non-surgical treatment options have been used. Bunion surgery has improved dramatically over the last 20 years but it still cannot guarantee a total recovery and often post operative complications such as calluses and corns can occur depending on the procedure used. If your bunion becomes painful, red and swollen, try using ice on the joint and elevate the foot on a stool. Bunion Night Splints can reduce the size of the bunion. This will straighten the bunion while you sleep. A Bunion Shield can reduce the pain over the bunion. Performing stretches on your toes and feet while you go about your daily routine. This increases circulation, red blood cell activity, and bone realignment. The easiest way to do this is by using a soft, flexible, medical grade gel Toe stretcher which is gentle between the toes and helps to straighten your toes. 
Surgical Treatment
When the pain of a bunion interferes with daily activities, and conservative treatment has been completed it's time to discuss surgical options. Foot Mechanics has excellent relationships with many Orthopaedic Surgeons, who are the specialists who perform bunion surgery. Because bunions are caused by faulty foot mechanics surgery can improve the look of your feet by removing the ?bump? but if the underlying mechanics are not addressed then the bunion is likely to return. For this reason orthotics are used post-surgery to prevent the return of bunions.
Calcaneal Apophysitis The Truth
Severs disease, also known as calcaneal apophysitis, is a condition in which the growth plate along the heel becomes inflamed. It most commonly occurs in active, early-teen children. Most patients with Severs disease complain of heel pain. In general the pain is exacerbated with increased activities, such as running, jumping, or climbing stairs. The pain often improves with a period of rest.
Causes
Sever's disease can result from standing too long, which puts constant pressure on the heel. Poor-fitting shoes can contribute to the condition by not providing enough support or padding for the feet or by rubbing against the back of the heel. Although Sever's disease can occur in any child, these conditions increase the chances of it happening. Pronated foot (a foot that rolls in at the ankle when walking), which causes tightness and twisting of the Achilles tendon, thus increasing its pull on the heel's growth plate, flat or high arch, which affects the angle of the heel within the foot, causing tightness and shortening of the Achilles tendon, short leg syndrome (one leg is shorter than the other), which causes the foot on the short leg to bend downward to reach the ground, pulling on the Achilles tendon, overweight or obesity, which puts weight-related pressure on the growth plate
Symptoms
Chief complaint is heel pain which increases pain during running and jumping activities. Pain is localized to the very posterior aspect of the heel. Pain is elicited only with weightbearing. Mild involvement is present if pain is brought on only with running during sports. The symptoms can be severe, with pain (and possibly limp) with activities of daily living (ie walking).
Diagnosis
Sever?s disease is diagnosed based on a doctor?s physical examination of the lower leg, ankle, and foot. If the diagnosis is in question, the doctor may order x-rays or an MRI to determine if there are other injuries that may be causing the heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment may consist of one or more of the following. Elevating the heel. Stretching hamstring and calf muscles 2-3 times daily. Using R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). Foot orthotics. Medication. Physical therapy. Icing daily (morning). Heating therapy. Open back shoe are best and avoid high heel shoe. The Strickland Protocol has shown a positive response in patients with a mean return to sport in less than 3 weeks. Further research into the anatomical and biomechanical responses of this protocol are currently being undertaken.
Treatment Of Partial Achilles Tendon Rupture
Overview
 The Achilles' tendon is located in the leg just behind and above the heel. As the connection between the heel and calf muscle, its function is to allow the bending of the foot downwards. Generally if there is a tear to the Achilles' tendon it will be known as a rupture. This can be a partial tear or a complete tear, although partial tears are much rarer.
The Achilles' tendon is located in the leg just behind and above the heel. As the connection between the heel and calf muscle, its function is to allow the bending of the foot downwards. Generally if there is a tear to the Achilles' tendon it will be known as a rupture. This can be a partial tear or a complete tear, although partial tears are much rarer.
Causes
The tendon usually ruptures without any warning. It is most common in men between the ages of 40-50, who play sports intermittently, such as badminton and squash. There was probably some degeneration in the tendon before the rupture which may or may not have been causing symptoms.
Symptoms
Many people say that a ruptured Achilles feels like ?being shot in the heel?, if you can imagine how enjoyable that feels. You may hear a snap sound or feel a sudden sharp pain when the tendon tears. After a few moments, the pain settles and the back of the lower leg aches. You can walk and bear weight, but you may find it difficult to point the foot downward or push off the ground on the affected side. You will be unable to stand on tiptoe. Bruising and swelling are likely, and persistent pain will be present. Similar symptoms may be caused by an inflamed Achilles tendon (Achilles tendonitis), a torn calf muscle, arthritis of the ankle, or deep vein thrombosis in the calf, so an MRI or ultrasound scan will likely be used to diagnose your condition.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made mostly by clinical examination with a defect usually noted on visual examination and by touching the area. A simple test can be done by squeezing the back of the calf with the foot resting in the air. Normally when squeezing the muscle belly the tendon will shorten causing the foot to move in a downward position. With a rupture this squeezing effect may show no movement of the foot if it is not attached properly. A negative test does not mean there isn't some degree of rupture as some of the tendon fibers may still be attached. Sometimes x-rays, an mri, or an ultrasound can be helpful in determining the extent of the rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain. Use support devices as directed. You may need crutches or a cane for support when you walk. These devices help decrease stress and pressure on your tendon. Your caregiver will tell you how much weight you can put on your leg. Ask for more information about how to use crutches or a cane correctly. Start activity as directed. Your caregiver will tell you when it is okay to walk and play sports. You may not be able to play sports for 6 months or longer. Ask when you can go back to work or school. Do not drive until your caregiver says it is okay. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be indicated directly following injury rather than conservative care. Repair of an achilles tendon rupture is greatly varied for each clinical situation. There may be a direct repair of the ends of the tendon with suture, or possibly a tendon graft used to augment the tendon. Post-operatively, the period of immobilization will depend on the size of the defect that was repaired and how it was completed. Usually the immobilization is between 6-10 weeks. This repair may allow for a complete return to normal function, but in many instances the healing is complicated with adhesions and a partial loss of range of motion. There may be a continued soft tissue defect noted and a permanent or prolonged swelling.
Prevention
Prevention centers on appropriate daily Achilles stretching and pre-activity warm-up. Maintain a continuous level of activity in your sport or work up gradually to full participation if you have been out of the sport for a period of time. Good overall muscle conditioning helps maintain a healthy tendon.
How To Assess Apparent Leg Length Discrepancy
Approximately 75% of us present with one leg longer than the other. It?s staggering, literally, that so many people walk about with an imbalance. Yet to have one leg longer than the other doesn?t seem to create pain for everyone but for those that it does it brings pain in a myriad of dysfunction from TMJ, headaches, low back pain, IBS, bladder problems, sexual dysfunction, sacroiliac joint pain, pubis dysfunction, groin strain, gluteal dysfunction as well as the formation of trigger points.

Causes
A number of causes may lead to leg length discrepancy in children. Differences in leg length frequently follow fractures in the lower extremities in children due to over or under stimulation of the growth plates in the broken leg. Leg length discrepancy may also be caused by a congenital abnormality associated with a condition called hemihypertrophy. Or it may result from neuromuscular diseases such as polio and cerebral palsy. Many times, no cause can be identified. A small leg length discrepancy of a quarter of an inch or less is quite common in the general population and of no clinical significance. Larger leg length discrepancies become more significant. The long-term consequences of a short leg may include knee pain, back pain, and abnormal gait or limp.
Symptoms
In addition to the distinctive walk of a person with leg length discrepancy, over time, other deformities may be noted, which help compensate for the condition. Toe walking on the short side to decrease the swaying during gait. The foot will supinate (high arch) on the shorter side. The foot will pronate (flattening of the arch) on the longer side. Excessive pronation leads to hypermobility and instability, resulting in metatarsus primus varus and associated unilateral juvenile hallux valgus (bunion) deformity.
Diagnosis
Asymmetry is a clue that a LLD is present. The center of gravity will shift to the short limb side and patients will try to compensate, displaying indications such as pelvic tilt, lumbar scoliosis, knee flexion, or unilateral foot pronation. Asking simple questions such as, "Do you favor one leg over the other?" or, "Do you find it uncomfortable to stand?" may also provide some valuable information. Performing a gait analysis will yield some clues as to how the patient compensates during ambulation. Using plantar pressure plates can indicate load pressure differences between the feet. It is helpful if the gait analysis can be video-recorded and played back in slow motion to catch the subtle aspects of movement.
Non Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment can be effective. A shoe lift may be recommended if the leg length difference is less than 1 inch. More significant leg length discrepancies may require a surgical procedure. In children, surgical procedures are available to help make leg lengths more equal.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.
What Can Cause Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) ?
Overview
The adult acquired flatfoot (AAF) is a progressive, symptomatic (painful) deformity resulting from gradual stretch (attenuation) of the tibialis posterior tendon as well as the ligaments that support the arch of the foot. Although the posterior tibialis tendon plays a significant role, this pathology has recently been recognized as involving failure of other interosseous ligaments, such as the spring ligament. Due to the complexity of this pathology, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is now referred to as adult acquired flatfoot. Severe flatfoot associated with AAF can lead to other problems, such as plantar fascial tension, tendon pain, rearfoot subluxation, and ankle osteoarthritis.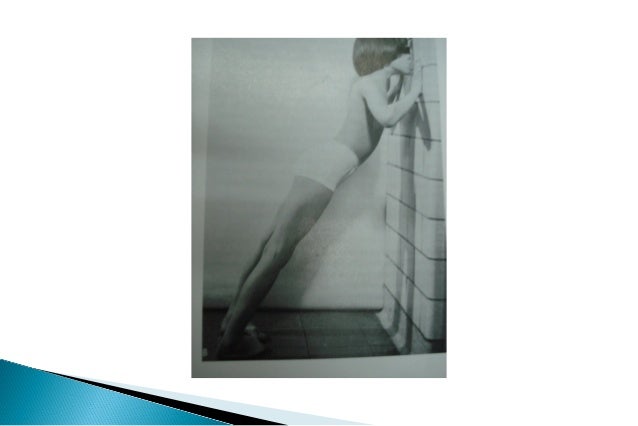 
Causes
There are a number of theories as to why the tendon becomes inflamed and stops working. It may be related to the poor blood supply within the tendon. Increasing age, inflammatory arthritis, diabetes and obesity have been found to be causes.
Symptoms
Symptoms shift around a bit, depending on what stage of PTTD you?re in. For instance, you?re likely to start off with tendonitis, or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon. This will make the area around the inside of your ankle and possibly into your arch swollen, reddened, warm to the touch, and painful. Inflammation may actually last throughout the stages of PTTD. The ankle will also begin to roll towards the inside of the foot (pronate), your heel may tilt, and you may experience some pain in your leg (e.g. shin splints). As the condition progresses, the toes and foot begin to turn outward, so that when you look at your foot from the back (or have a friend look for you, because-hey-that can be kind of a difficult maneuver to pull off) more toes than usual will be visible on the outside (i.e. the side with the pinky toe). At this stage, the foot?s still going to be flexible, although it will likely have flattened somewhat due to the lack of support from the posterior tibial tendon. You may also find it difficult to stand on your toes. Finally, you may reach a stage in which your feet are inflexibly flat. At this point, you may experience pain below your ankle on the outside of your foot, and you might even develop arthritis in the ankle.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction and AAFD is usually made from a combination of symptoms, physical exam and x-ray imaging. The location of pain, shape of the foot, flexibility of the hindfoot joints and gait all may help your physician make the diagnosis and also assess how advanced the problem is.
Non surgical Treatment
Flatfoot deformity can be treated conservatively or with surgical intervention depending on the severity of the condition. When people notice their arches flattening, they should immediately avoid non-supportive shoes such as flip-flops, sandals or thin-soled tennis shoes. Theses shoes will only worsen the flatfoot deformity and exacerbate arch pain. Next, custom orthotics are essential for people with collapsed arches. Over-the-counter insoles only provide cushion and padding to the arch, whereas custom orthotics are fabricated to specifically fit the patient?s foot and provide support in the arch where the posterior tibial tendon is unable to anymore. Use of custom orthotics in the early phases of flatfoot or PTTD can prevent worsening of symptoms and prevent further attenuation or injury to the posterior tibial tendon. In more severe cases of flatfoot deformity an ankle foot orthosis (AFO) such as a Ritchie brace is needed. This brace provides more support to the arch and hindfoot rather than an orthotic but can be bulky in normal shoegear. Additional treatment along with use of custom orthotics is use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDS) such as Advil, Motrin, or Ibuprofen which can decrease inflammation to the posterior tibial tendon. If pain is severe, the patient may need to be placed in a below the knee air walker boot for several weeks which will allow the tendon to rest and heal, especially if a posterior tibial tendon tear is noted on MRI. 
Surgical Treatment
If surgery is necessary, a number of different procedures may be considered. The specifics of the planned surgery depend upon the stage of the disorder and the patient?s specific goals. Procedures may include ligament and muscle lengthening, removal of the inflamed tendon lining, tendon transfers, cutting and realigning bones, placement of implants to realign the foot and joint fusions. In general, early stage disease may be treated with tendon and ligament (soft-tissue) procedures with the addition of osteotomies to realign the foot. Later stage disease with either a rigidly fixed deformity or with arthritis is often treated with fusion procedures. If you are considering surgery, your doctor will speak with about the specifics of the planned procedure.
What Exactly Is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction ?
Overview
Adult flatfoot may be due to multiple problems including a dysfunctional posterior tibial tendon (PTT), hypermobility and ligamentous laxity, or possibly a coalition that becomes symptomatic. For a vast majority of patients, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is the cause of symptomatic flatfoot and is the main trigger of surgical reconstruction in flatfoot. The common presenting scenario for adult flatfoot is a case of unilateral flatfoot with pain. Patients will often confirm they ?always had flat feet? but have noticed increased pain and additional collapse in the past few months to years. They may also note increased swelling and a possible concern over one foot increasing in shoe size. After a comprehensive dermatologic, neurologic and vascular assessment, one should direct his or her attention to the musculoskeletal portion of the exam. It is key to examine the foot and leg as a whole in order to determine the proper procedure and consider each phase of the corrective surgery. 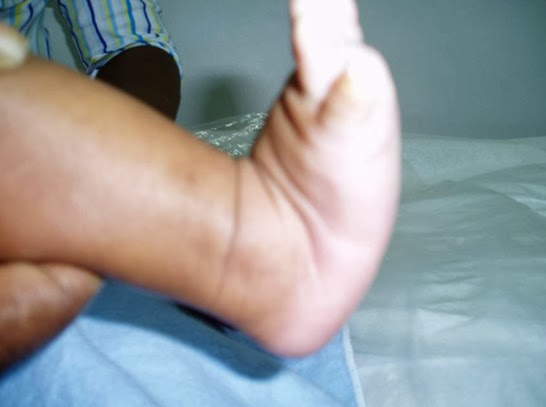
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis This type of arthritis attacks the cartilage in the foot, leading to pain and flat feet. It is caused by auto-immune disease, where the body?s immune system attacks its own tissues. Diabetes. Having diabetes can cause nerve damage and affect the feeling in your feet and cause arch collapse. Bones can also fracture but some patients may not feel any pain due to the nerve damage. Obesity and/or hypertension (high blood pressure) This increases your risk of tendon damage and resulting flat foot.
Symptoms
Often, this condition is only present in one foot, but it can affect both. Adult acquired flatfoot symptoms vary, but can swelling of the foot's inner side and aching heel and arch pain. Some patients experience no pain, but others may experience severe pain. Symptoms may increase during long periods of standing, resulting in fatigue. Symptoms may change over time as the condition worsens. The pain may move to the foot's outer side, and some patients may develop arthritis in the ankle and foot.
Diagnosis
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is diagnosed with careful clinical observation of the patient?s gait (walking), range of motion testing for the foot and ankle joints, and diagnostic imaging. People with flatfoot deformity walk with the heel angled outward, also called over-pronation. Although it is normal for the arch to impact the ground for shock absorption, people with PTTD have an arch that fully collapses to the ground and does not reform an arch during the entire gait period. After evaluating the ambulation pattern, the foot and ankle range of motion should be tested. Usually the affected foot will have decreased motion to the ankle joint and the hindfoot. Muscle strength may also be weaker as well. An easy test to perform for PTTD is the single heel raise where the patient is asked to raise up on the ball of his or her effected foot. A normal foot type can lift up on the toes without pain and the heel will invert slightly once the person has fully raised the heel up during the test. In early phases of PTTD the patient may be able to lift up the heel but the heel will not invert. An elongated or torn posterior tibial tendon, which is a mid to late finding of PTTD, will prohibit the patient from fully rising up on the heel and will cause intense pain to the arch. Finally diagnostic imaging, although used alone cannot diagnose PTTD, can provide additional information for an accurate diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. Xrays of the foot can show the practitioner important angular relationships of the hindfoot and forefoot which help diagnose flatfoot deformity. Most of the time, an MRI is not needed to diagnose PTTD but is a tool that should be considered in advanced cases of flatfoot deformity. If a partial tear of the posterior tibial tendon is of concern, then an MRI can show the anatomic location of the tear and the extensiveness of the injury.
Non surgical Treatment
Stage one deformities usually respond to conservative or non-surgical therapy such as anti-inflammatory medication, casting, functional orthotics or a foot ankle orthosis called a Richie Brace. If these modalities are unsuccessful surgery is warranted. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment should be considered when all other conservative treatment has failed. Surgery options for flatfoot reconstruction depend on the severity of the flatfoot. Surgery for a flexible flatfoot deformity (flatfoot without arthritis to the foot joints) involves advancing the posterior tibial tendon under the arch to provide more support and decrease elongation of the tendon as well as addressing the hindfoot eversion with a osteotomy to the calcaneus (surgical cut in the heel bone). Additionally, the Achilles tendon may need to be lengthened because of the compensatory contracture of the Achilles tendon with flatfoot deformity. Flatfoot deformity with arthritic changes to the foot is considered a rigid flatfoot. Correction of a rigid flatfoot deformity usually involves surgical fusion of the hindfoot joints. This is a reconstructive procedure which allows the surgeon to re-position the foot into a normal position. Although the procedure should be considered for advanced PTTD, it has many complications and should be discussed at length with your doctor.